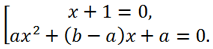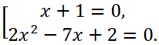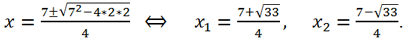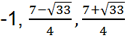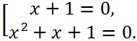Symmetric equations of the 3 degree have the form: ax
3 + bx
2 + bx + a = 0, a ≠ 0.
The polynomial on the left side of such equations can always be factorized as follows:
ax
3 + bx
2 + bx + a = a(x
3 + 1) + bx(x + 1) =
= a(x + 1)(x
2 - x + 1) + bx(x + 1) = (x + 1)(ax
2 + (b - a)x + a).
Therefore, the original equation is equivalent to a set of equations:
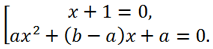
Thus, the solution of the original equation is always the number -1, and the remaining roots are the roots of the quadratic equation ax
2 + (b - a)x + a = 0.
Let's consider the solution of symmetric equations of degree 3 using examples.
Examples of solving symmetric cubic equations
Example 1.
Solve the equation 2x
3 - 5x
2 - 5x + 2 = 0.
Solution.
Factorize the left side of the original equation:
2x
3 - 5x
2 - 5x + 2 = 2(x + 1)(x
2 - x + 1) - 5x(x + 1) = (x + 1)(2x
2 - 2x + 2 - 5x) = (x + 1)(2x
2 - 7x + 2).
So, the original equation is equivalent to the set
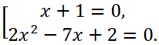
the first equation of the set has a root of -1, the second equation is solved using the formulas for the roots of a quadratic equation:
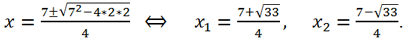 Answer:
Answer: 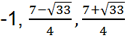 Example 2.
Example 2.
Find the real roots of the equation x
3 + 2x
2 + 2x + 1 = 0.
Solution. x
3 + 2x
2 + 2x + 1 = (x + 1)(x
2 - x + 1) + 2x(x + 1) = (x + 1)(x
2 - x + 1 + 2x) = (x + 1)(x
2 + x + 1).
So, the original equation is equivalent to the set
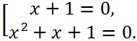
The first equation of the set has a root of -1, the second equation has no real roots, since the discriminant D = 1 - 4 = -3 < 0.
Answer: -1.