Vector definition, absolute value, or modulus of a vector
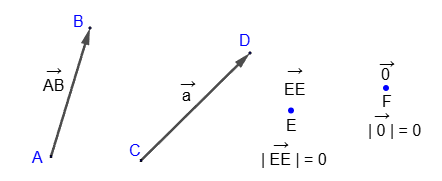
A vector is a directed segment. The direction of a vector is determined by specifying its beginning and end. A vector is denoted by two capital letters (the first letter represents the beginning, and the second letter represents the end) or by a single lowercase letter with a line or arrow above it.
If the beginning of a vector coincides with its end (i.e., it is a point), then such a vector is called a zero vector.
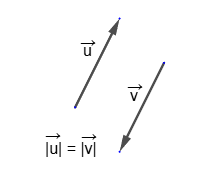
The absolute value or modulus of a vector is the length of the segment representing the vector. The length of a zero vector is considered to be zero.
A unit vector is a vector whose length is equal to one.
Collinear vectors
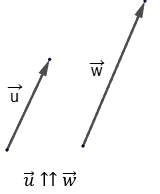
Nonzero vectors are called collinear if they lie either on the same line or on parallel lines. The zero vector is considered collinear with any other vector.
If collinear vectors are directed in the same direction, they are called codirectional:
The zero vector has no direction, so the zero vector is considered to be codirectional with any vector.
If collinear vectors are directed in opposite directions, they are called oppositely directed:
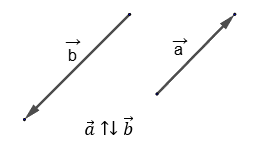
 A unit vector is a vector whose length is equal to one.
A unit vector is a vector whose length is equal to one. The zero vector has no direction, so the zero vector is considered to be codirectional with any vector.
The zero vector has no direction, so the zero vector is considered to be codirectional with any vector.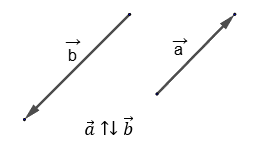
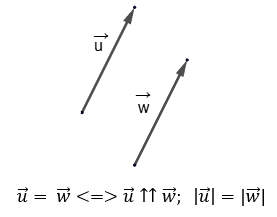 From the definition of equality of vectors it follows that equal vectors completely coincide under parallel shift.
From the definition of equality of vectors it follows that equal vectors completely coincide under parallel shift.