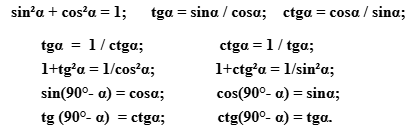The sine, cosine, tangent, and cotangent of an acute angle of a rectangular triangle
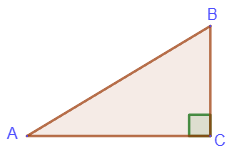
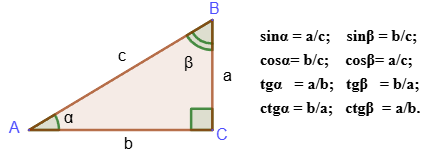
The opposite leg for ∠A is the leg BC, the adjacent leg is the leg AC. Accordingly, for ∠B the opposite leg is the leg AC, and the adjacent leg is the leg BC.
1. The sine of an acute angle of a rectangular triangle is the ratio of the opposite leg to the hypotenuse: sin∠A=BC/AB.
2. The cosine of an acute angle of a rectangular triangle is the ratio of the adjacent leg to the hypotenuse: cos∠A=AC/AB.
3. The tangent of an acute angle of a rectangular triangle is the ratio of the opposite leg to the adjacent leg: tg∠A=BC/AC.
4. The cotangent of an acute angle of a rectangular triangle is the ratio of the adjacent leg to the opposite leg: ctg∠A=AC/BC.
Sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent of an angle depend only on the size of the angle and do not depend on the size and location of the triangle.
Basic trigonometric formulas:
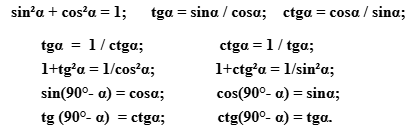
Values of trigonometric functions of angles 30°, 45°, 60°.
1. The angle 30°:
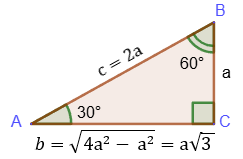
sin30° = a/2a = 1/2; cos30° = √3/2; tg30° = 1/√3; ctg30° = √3.
2. The angle 60°:
sin60° = √3/2; cos60° = √1/2; tg60° = √3; ctg60° = 1/√3.
3. The angle 45°:
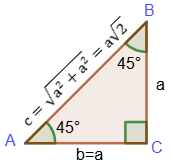
sin45° = √2/2; cos45° = √2/2; tg45° = 1; ctg45° = 1.
 The opposite leg for ∠A is the leg BC, the adjacent leg is the leg AC. Accordingly, for ∠B the opposite leg is the leg AC, and the adjacent leg is the leg BC.
1. The sine of an acute angle of a rectangular triangle is the ratio of the opposite leg to the hypotenuse: sin∠A=BC/AB.
2. The cosine of an acute angle of a rectangular triangle is the ratio of the adjacent leg to the hypotenuse: cos∠A=AC/AB.
3. The tangent of an acute angle of a rectangular triangle is the ratio of the opposite leg to the adjacent leg: tg∠A=BC/AC.
4. The cotangent of an acute angle of a rectangular triangle is the ratio of the adjacent leg to the opposite leg: ctg∠A=AC/BC.
Sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent of an angle depend only on the size of the angle and do not depend on the size and location of the triangle.
The opposite leg for ∠A is the leg BC, the adjacent leg is the leg AC. Accordingly, for ∠B the opposite leg is the leg AC, and the adjacent leg is the leg BC.
1. The sine of an acute angle of a rectangular triangle is the ratio of the opposite leg to the hypotenuse: sin∠A=BC/AB.
2. The cosine of an acute angle of a rectangular triangle is the ratio of the adjacent leg to the hypotenuse: cos∠A=AC/AB.
3. The tangent of an acute angle of a rectangular triangle is the ratio of the opposite leg to the adjacent leg: tg∠A=BC/AC.
4. The cotangent of an acute angle of a rectangular triangle is the ratio of the adjacent leg to the opposite leg: ctg∠A=AC/BC.
Sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent of an angle depend only on the size of the angle and do not depend on the size and location of the triangle.
 Basic trigonometric formulas:
Basic trigonometric formulas: