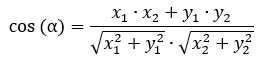The angle between vectors
Let two non-collinear vectors be given
and
. Let's set aside both of these vectors from the same point in the plane. The angle between two vectors is the minimum angle from 0° до 180°, by which one of them must be rotated so that the directions of the vectors coincide.
If the vectors are co-directional, then the angle between them is 0°, if they are oppositely directed, then the angle between them is 180°. If one of the vectors or both vectors are zero, then the angle between them is considered to be zero.
The angle between vectors
and
is denoted by
.
Scalar product of vectors and its properties
The scalar product of two vectors is a number equal to the product of the lengths of these vectors by the cosine of the angle between them:
If the vectors
and
are perpendicular, then
and hence,
.
Conversely, if
and
are nonzero, and
,
then it follows from the definition of the scalar product that
.
Thus, a necessary and sufficient condition for the perpendicularity of two vectors is that their scalar product is equal to zero.
From the definition of the scalar product for non-zero vectors it follows that if the angle between the vectors is acute, then the scalar product is a positive number; if the angle is obtuse, then it is negative.
If the angle between the vectors is zero, then
.
It follows that
2.
If the angle between vectors 180°, then
.
Obviously, for any vectors
,
,
and an arbitrary number q, the scalar product has the following properties:
1)
;
2)
;
3)
.

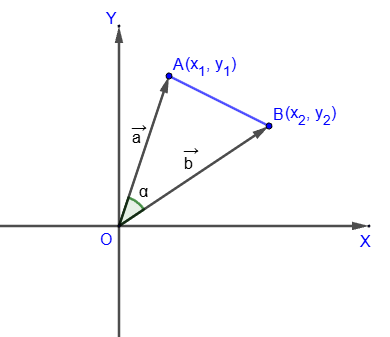 By the cosine theorem
By the cosine theorem
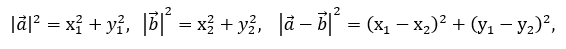 after the appropriate transformations, we obtain the formula for the scalar product in coordinates:
Obviously, this formula is also valid for zero vectors and , and for collinear vectors.
after the appropriate transformations, we obtain the formula for the scalar product in coordinates:
Obviously, this formula is also valid for zero vectors and , and for collinear vectors.